Monday, 30 December 2019
rotate images
Friday, 20 December 2019
Thursday, 19 December 2019
Codeigniter validation for rest API.
first set data
$this->form_validation->set_data($data);
then set rules.
$this->form_validation->set_rules('job_id','job_id', 'required');
Wednesday, 18 December 2019
squlize with express js
http://zetcode.com/javascript/sequelize/
https://sequelize.org/master/manual/raw-queries.html
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20460270/how-to-make-join-queries-using-sequelize-on-node-js
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23361022/sequelize-in-nodejs-inner-join-implementation-failure
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31983885/create-multiple-inner-joins-with-sequelize-orm
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27465850/typeerror-router-use-requires-middleware-function-but-got-a-object
how to do join query in sequlize
node js jwt login exapmle
- router.post('/login, function(req, res) {
- // find the user
- User.findOne({
- name: req.body.username
- }, function(err, res) {
- if (err) throw err;
- if (!res) {
- res.json({ success: false, message: Login failed.' });
- } else if (res) {
- // check if password matches
- if (res.password != req.body.password) {
- res.json({ success: false, message: Login failed. Wrong password.' });
- } else {
- var token = jwt.sign(res, app.get('superSecret'), {
- expiresInMinutes: 1600
- });
- // return the information including token as JSON
- res.json({
- success: true,
- message: 'Valid token!',
- token: token
- });
- }
- } });
- });
- jwt = require("express-jwt");
- app.use(function(req, res, next) {
- var token = req.body.token || req.query.token || req.headers['x-access-token'];
- if (token) {
- jwt.verify(token, app.get('superSecret'), function(err, decoded) {
- if (err) {
- return res.json({ success: false, message: 'Invalid token.' });
- } else {
- req.decoded = decoded;
- next();
- }
- });
- } else {
- return res.status(403).send({
- success: false,
- message: 'No token given.'
- });
- }
- });
allow crossorigin in express js
Differnce between aws cognito user poll and and identity poll
identity poll - Identity pool use user pool token to authenticate and return aws credential to use aws services like lambda dynamodb s3 .
Tuesday, 17 December 2019
Creating seprate route and use it
Java demonstration for s3 manupulation
/*
* Copyright 2010-2013 Amazon.com, Inc. or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License").
* You may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* A copy of the License is located at
*
* http://aws.amazon.com/apache2.0
*
* or in the "license" file accompanying this file. This file is distributed
* on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either
* express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing
* permissions and limitations under the License.
*/
package com.amazonaws.samples;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.Writer;
import java.util.UUID;
import com.amazonaws.AmazonClientException;
import com.amazonaws.AmazonServiceException;
import com.amazonaws.regions.Region;
import com.amazonaws.regions.Regions;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.AmazonS3Client;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.Bucket;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.GetObjectRequest;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.ListObjectsRequest;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.ObjectListing;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.PutObjectRequest;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.S3Object;
import com.amazonaws.services.s3.model.S3ObjectSummary;
/**
* This sample demonstrates how to make basic requests to Amazon S3 using
* the AWS SDK for Java.
* <p>
* <b>Prerequisites:</b> You must have a valid Amazon Web Services developer
* account, and be signed up to use Amazon S3. For more information on
* Amazon S3, see http://aws.amazon.com/s3.
* <p>
* <b>Important:</b> Be sure to fill in your AWS access credentials in
* ~/.aws/credentials (C:\Users\USER_NAME\.aws\credentials for Windows
* users) before you try to run this sample.
*/
public class S3Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* Create your credentials file at ~/.aws/credentials (C:\Users\USER_NAME\.aws\credentials for Windows users)
* and save the following lines after replacing the underlined values with your own.
*
* [default]
* aws_access_key_id = YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID
* aws_secret_access_key = YOUR_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
*/
AmazonS3 s3 = new AmazonS3Client();
Region usWest2 = Region.getRegion(Regions.US_WEST_2);
s3.setRegion(usWest2);
String bucketName = "my-first-s3-bucket-" + UUID.randomUUID();
String key = "MyObjectKey";
System.out.println("===========================================");
System.out.println("Getting Started with Amazon S3");
System.out.println("===========================================\n");
try {
/*
* Create a new S3 bucket - Amazon S3 bucket names are globally unique,
* so once a bucket name has been taken by any user, you can't create
* another bucket with that same name.
*
* You can optionally specify a location for your bucket if you want to
* keep your data closer to your applications or users.
*/
System.out.println("Creating bucket " + bucketName + "\n");
s3.createBucket(bucketName);
/*
* List the buckets in your account
*/
System.out.println("Listing buckets");
for (Bucket bucket : s3.listBuckets()) {
System.out.println(" - " + bucket.getName());
}
System.out.println();
/*
* Upload an object to your bucket - You can easily upload a file to
* S3, or upload directly an InputStream if you know the length of
* the data in the stream. You can also specify your own metadata
* when uploading to S3, which allows you set a variety of options
* like content-type and content-encoding, plus additional metadata
* specific to your applications.
*/
System.out.println("Uploading a new object to S3 from a file\n");
s3.putObject(new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, key, createSampleFile()));
/*
* Download an object - When you download an object, you get all of
* the object's metadata and a stream from which to read the contents.
* It's important to read the contents of the stream as quickly as
* possibly since the data is streamed directly from Amazon S3 and your
* network connection will remain open until you read all the data or
* close the input stream.
*
* GetObjectRequest also supports several other options, including
* conditional downloading of objects based on modification times,
* ETags, and selectively downloading a range of an object.
*/
System.out.println("Downloading an object");
S3Object object = s3.getObject(new GetObjectRequest(bucketName, key));
System.out.println("Content-Type: " + object.getObjectMetadata().getContentType());
displayTextInputStream(object.getObjectContent());
/*
* List objects in your bucket by prefix - There are many options for
* listing the objects in your bucket. Keep in mind that buckets with
* many objects might truncate their results when listing their objects,
* so be sure to check if the returned object listing is truncated, and
* use the AmazonS3.listNextBatchOfObjects(...) operation to retrieve
* additional results.
*/
System.out.println("Listing objects");
ObjectListing objectListing = s3.listObjects(new ListObjectsRequest()
.withBucketName(bucketName)
.withPrefix("My"));
for (S3ObjectSummary objectSummary : objectListing.getObjectSummaries()) {
System.out.println(" - " + objectSummary.getKey() + " " +
"(size = " + objectSummary.getSize() + ")");
}
System.out.println();
/*
* Delete an object - Unless versioning has been turned on for your bucket,
* there is no way to undelete an object, so use caution when deleting objects.
*/
System.out.println("Deleting an object\n");
s3.deleteObject(bucketName, key);
/*
* Delete a bucket - A bucket must be completely empty before it can be
* deleted, so remember to delete any objects from your buckets before
* you try to delete them.
*/
System.out.println("Deleting bucket " + bucketName + "\n");
s3.deleteBucket(bucketName);
} catch (AmazonServiceException ase) {
System.out.println("Caught an AmazonServiceException, which means your request made it "
+ "to Amazon S3, but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message: " + ase.getMessage());
System.out.println("HTTP Status Code: " + ase.getStatusCode());
System.out.println("AWS Error Code: " + ase.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Error Type: " + ase.getErrorType());
System.out.println("Request ID: " + ase.getRequestId());
} catch (AmazonClientException ace) {
System.out.println("Caught an AmazonClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with S3, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message: " + ace.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* Creates a temporary file with text data to demonstrate uploading a file
* to Amazon S3
*
* @return A newly created temporary file with text data.
*
* @throws IOException
*/
private static File createSampleFile() throws IOException {
File file = File.createTempFile("aws-java-sdk-", ".txt");
file.deleteOnExit();
Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file));
writer.write("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz\n");
writer.write("01234567890112345678901234\n");
writer.write("!@#$%^&*()-=[]{};':',.<>/?\n");
writer.write("01234567890112345678901234\n");
writer.write("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz\n");
writer.close();
return file;
}
/**
* Displays the contents of the specified input stream as text.
*
* @param input
* The input stream to display as text.
*
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void displayTextInputStream(InputStream input) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(input));
while (true) {
String line = reader.readLine();
if (line == null) break;
System.out.println(" " + line);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Sunday, 15 December 2019
node js express debugging tutorial
Shift + Cmd + p
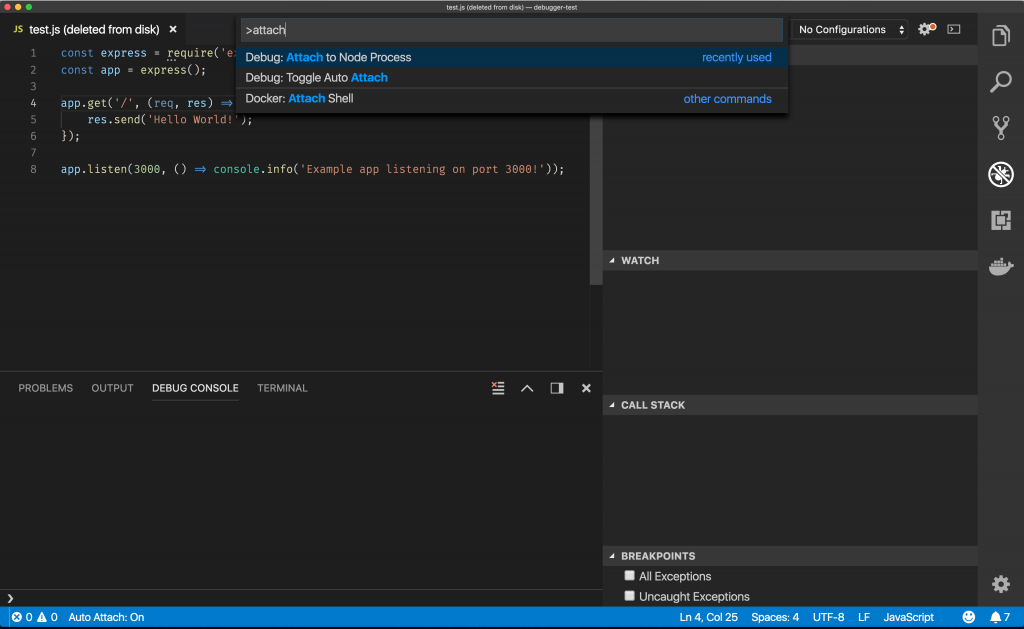
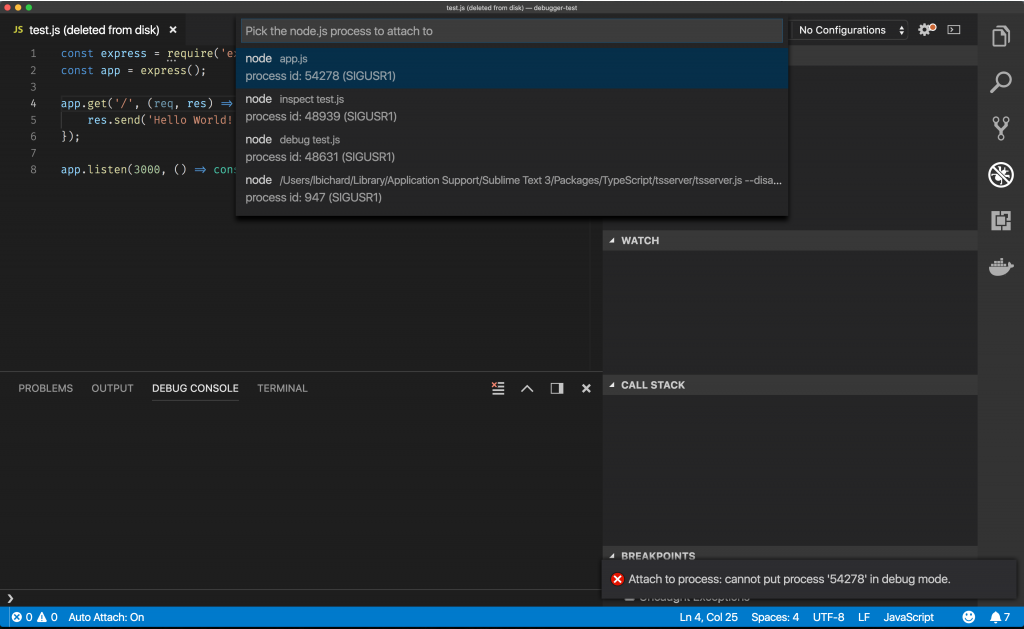
Debugger listening on ws://127.0.0.1:9229/d5efc834-41ae-4758-a9e6-4d8767c5752a
Wednesday, 11 December 2019
aws s3 content type
ContentType: 'image/jpeg'
When an image stored in an AWS S3 bucket is downloaded instead of being rendered in the browser, it's usually due to incorrect Content-Type settings or S3 permissions.
Possible Reasons & Fixes
1️⃣ Content-Type is Incorrect
If the Content-Type is not set properly, the browser doesn't recognize the file as an image and downloads it instead of displaying it.
✅ Fix: Ensure Correct Content-Type when Uploading
When uploading the image to S3, specify the correct MIME type (image/jpeg, image/png, etc.).
Example: Uploading with Correct Content-Type (Java AWS SDK v2)
javaimport software.amazon.awssdk.services.s3.S3Client;
import software.amazon.awssdk.services.s3.model.PutObjectRequest;
import software.amazon.awssdk.core.sync.RequestBody;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class S3Upload {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S3Client s3 = S3Client.create();
String bucketName = "your-bucket-name";
String key = "images/my-image.jpg";
PutObjectRequest putRequest = PutObjectRequest.builder()
.bucket(bucketName)
.key(key)
.contentType("image/jpeg") // Set proper Content-Type
.build();
s3.putObject(putRequest, RequestBody.fromFile(Paths.get("local-image.jpg")));
System.out.println("Image uploaded successfully!");
}
}
👉 If your image is already uploaded, update the metadata manually in the AWS S3 console:
- Go to the S3 bucket.
- Select the image file.
- Click Properties → Metadata.
- Add
Content-Type = image/jpeg(orimage/png). - Save changes.
2️⃣ Incorrect S3 Object Permissions
If the S3 object is not publicly accessible, the browser may not be able to load it properly.
✅ Fix: Make the Image Public
If your images should be public:
- Go to AWS S3 Console.
- Select the bucket and then the image file.
- Click Permissions → Public access.
- Enable public read access.
Or, if using Java SDK:
javaPutObjectRequest putRequest = PutObjectRequest.builder()
.bucket(bucketName)
.key(key)
.acl("public-read") // Makes the image publicly accessible
.contentType("image/jpeg")
.build();
3️⃣ Force Browser to Display the Image
Even if the Content-Type is correct, S3 may send a Content-Disposition header that forces a download.
✅ Fix: Remove Content-Disposition: attachment
If S3 sends this header, the browser will force a download instead of rendering the image.
To prevent this, remove or set Content-Disposition as inline:
javaPutObjectRequest putRequest = PutObjectRequest.builder()
.bucket(bucketName)
.key(key)
.contentType("image/jpeg")
.contentDisposition("inline") // Force the browser to display the image
.build();
This ensures that images open in the browser instead of being downloaded.
Final Check: Open Image in Browser
After making these fixes, test your image directly in the browser:
🔗 URL Format:
pgsqlhttps://your-bucket-name.s3.amazonaws.com/path-to-image.jpg
✅ If the image displays in the browser, everything is working! 🚀
Would you like help configuring AWS S3 bucket permissions using IAM policies? 😊